Provision ACK Resources
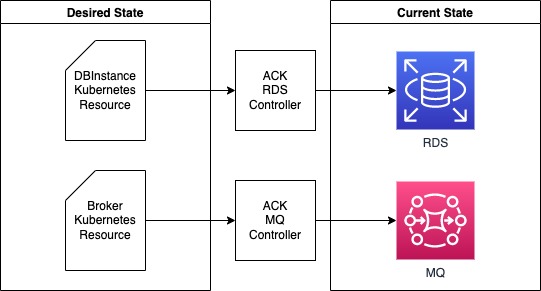
By default the catalog component in the sample application uses a MySQL database running as a pod in the EKS cluster. In this lab, we'll provision an Amazon RDS database for our application using Kubernetes custom resources to specify the desired configuration required by the workload.
The first thing we need to do is create a Kubernetes secret that'll be used to provide the master password for the RDS database. We'll configure ACK to read this secret as a source for the password:
secret/catalog-rds-pw created
Now let's explore the various ACK resources that we'll create. The first is an EC2 security group that will be applied to control access to the RDS database, which is done with a SecurityGroup resource:
apiVersion: ec2.services.k8s.aws/v1alpha1
kind: SecurityGroup
metadata:
name: $(EKS_CLUSTER_NAME)-catalog-ack
namespace: catalog
spec:
description: SecurityGroup
name: $(EKS_CLUSTER_NAME)-catalog-ack
vpcID: $(VPC_ID)
ingressRules:
- ipProtocol: tcp
ipRanges:
- cidrIP: "$(VPC_CIDR)"
fromPort: 3306
toPort: 3306
The EC2 security group above allows any traffic from the CIDR range of the VPC used by the EKS cluster. This has been done to keep the example clear and understandable. A more secure approach would be to use Security Groups for Pods to allow traffic from specific pods.
Next we want the RDS database to use the private subnets in our VPC. To accomplish this, we'll create a DBSubnetGroup which selects the appropriate subnet IDs:
apiVersion: rds.services.k8s.aws/v1alpha1
kind: DBSubnetGroup
metadata:
name: $(EKS_CLUSTER_NAME)-catalog-ack
namespace: catalog
spec:
description: DBSubnet group
name: $(EKS_CLUSTER_NAME)-catalog-ack
subnetIDs:
- $(VPC_PRIVATE_SUBNET_ID_1)
- $(VPC_PRIVATE_SUBNET_ID_2)
- $(VPC_PRIVATE_SUBNET_ID_3)
Finally, we can create the configuration for the RDS database itself with a DBInstance resource:
apiVersion: rds.services.k8s.aws/v1alpha1
kind: DBInstance
metadata:
name: $(EKS_CLUSTER_NAME)-catalog-ack
namespace: catalog
spec:
allocatedStorage: 20
dbInstanceClass: db.t4g.micro
dbInstanceIdentifier: $(EKS_CLUSTER_NAME)-catalog-ack
engine: mysql
engineVersion: "8.0"
masterUsername: "admin"
dbSubnetGroupRef:
from:
name: $(EKS_CLUSTER_NAME)-catalog-ack
vpcSecurityGroupRefs:
- from:
name: $(EKS_CLUSTER_NAME)-catalog-ack
masterUserPassword:
namespace: catalog
name: catalog-rds-pw
key: password
dbName: catalog
Apply this configuration to the Amazon EKS cluster:
securitygroup.ec2.services.k8s.aws/rds-eks-workshop created
dbinstance.rds.services.k8s.aws/rds-eks-workshop created
dbsubnetgroup.rds.services.k8s.aws/rds-eks-workshop created
The ACK controllers in the cluster will react to these new resources and provision the AWS infrastructure it has expressed. For example, we can use the AWS CLI to query the RDS database:
It takes some time to provision the AWS managed services, in the case of RDS up to 10 minutes. The AWS provider controller will report the status of the reconciliation in the status field of the Kubernetes custom resources.
We can use this status field to instruct kubectl to wait until the RDS database has been successfully created:
dbinstances.rds.services.k8s.aws/rds-eks-workshop condition met