Initial setup
Argo CD applies the GitOps methodology to Kubernetes. It uses Git as a source of truth for your cluster's desired state. You can use Argo CD to deploy applications, monitor their health, and sync them with the desired state. Kubernetes manifests can be specified in several ways:
- Kustomize applications
- Helm charts
- Jsonnet files
- Plain directories of Kubernetes YAML files
In this lab exercise, we will deploy an applications specified in Kustomize using Argo CD. We will use the ui application from EKS Workshop repository.
The Git repository in AWS CodeCommit has already been created for you.
If you want to use your own GitHub private repository you could re define
export GITOPS_REPO_URL_ARGOCD=https://github.com/username/reponame
and use those instructions to create an Argo CD secret to give access to the Git repository from Argo CD
Let's clone the Git repository.
Switched to a new branch 'main'
Create an Argo CD secret to give access to the Git repository from Argo CD:
Repository 'ssh://...' added
Argo CD application is a CRD Kubernetes resource object representing a deployed application instance in an environment. It defines key information about the application, such as the application name, the Git repository, and the path to the Kubernetes manifests. The application resource also defines the desired state of the application, such as the target revision, the sync policy, and the health check policy.
As the next step let's create an Argo CD Application which Sync with desired state in the Git repository:
application 'apps' created
Verify that the application has been created:
NAME CLUSTER NAMESPACE PROJECT STATUS HEALTH SYNCPOLICY CONDITIONS
argocd/apps https://kubernetes.default.svc default Synced Healthy <none> <none>
We can also see this Application in the ArgoCD UI now:
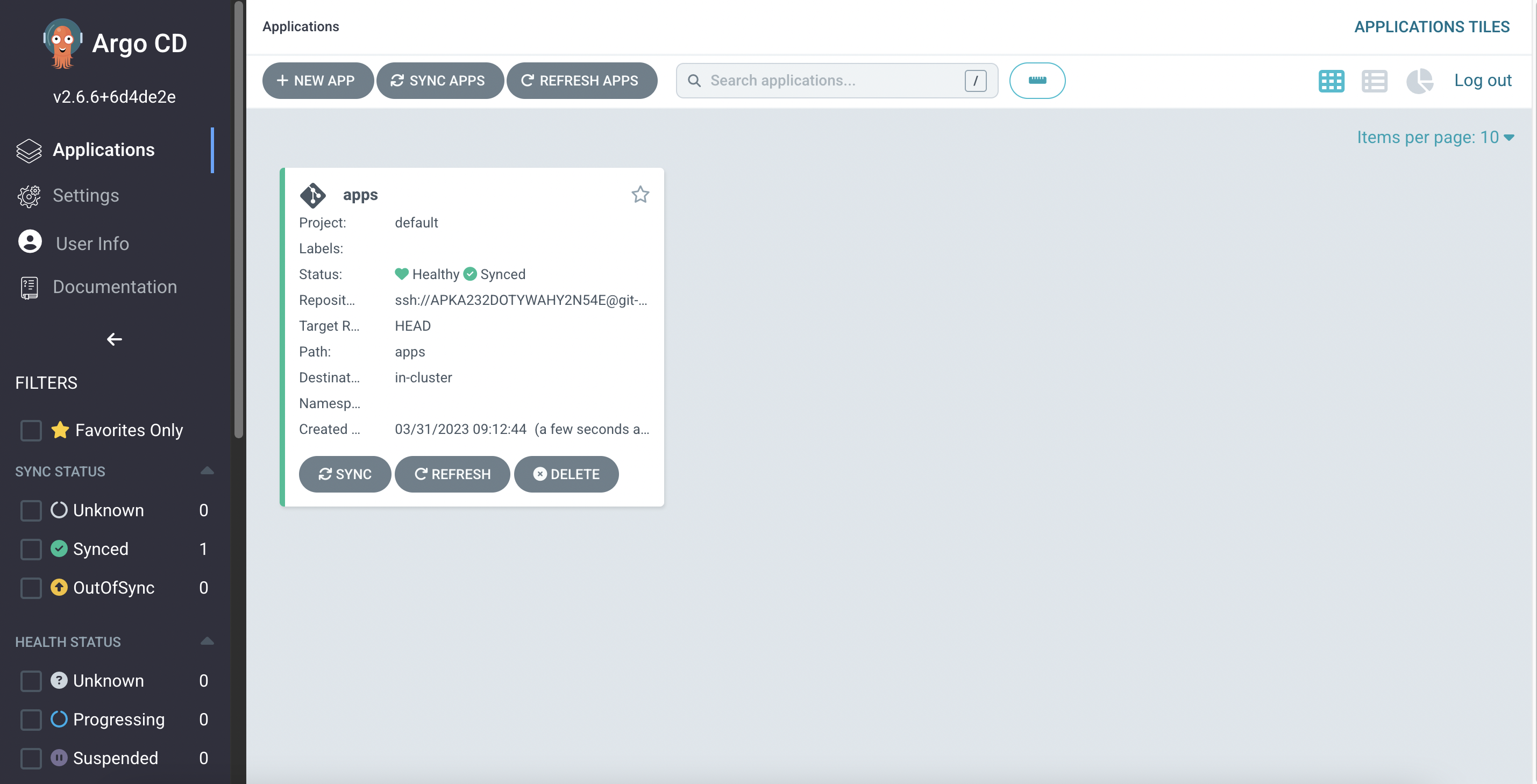
Alternatively, you can also interact with Argo CD objects in the cluster using the kubectl command:
NAME SYNC STATUS HEALTH STATUS
apps Synced Healthy